Atrial tachycardia A type of arrhythmia that begins in the hearts upper chambers the atria and causes a very fast heart rate of 160 to 200 beats a minute. This allows the blood to be pumped out of the ventricles and into the aorta and pulmonary trunk.
Exploring The Inner Workings Of The Heart S Electrical System
During the first few microseconds of the first stroke a large inductive voltage drop occurs from the top to the bottom of the building.

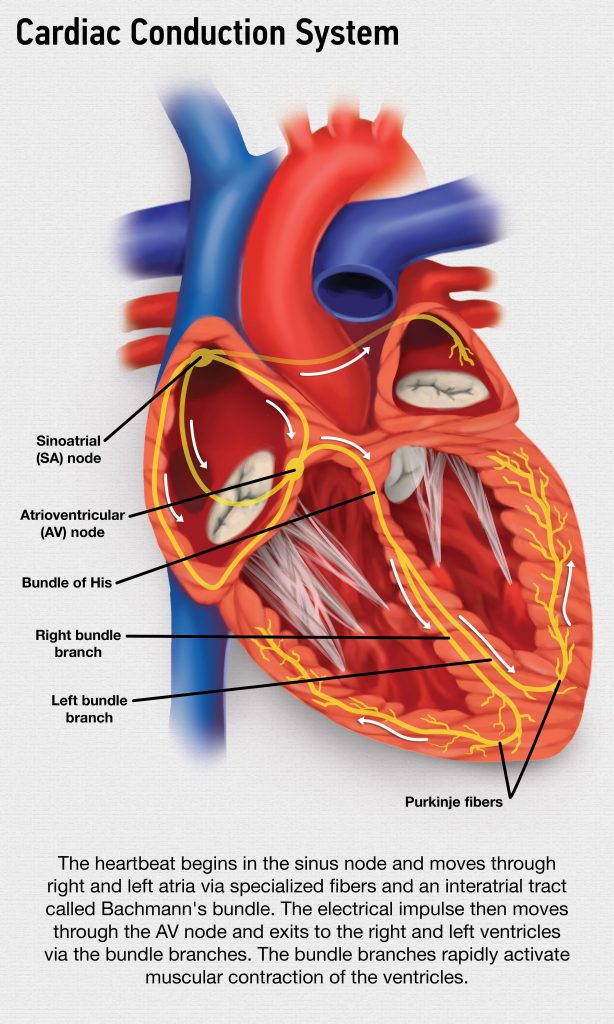
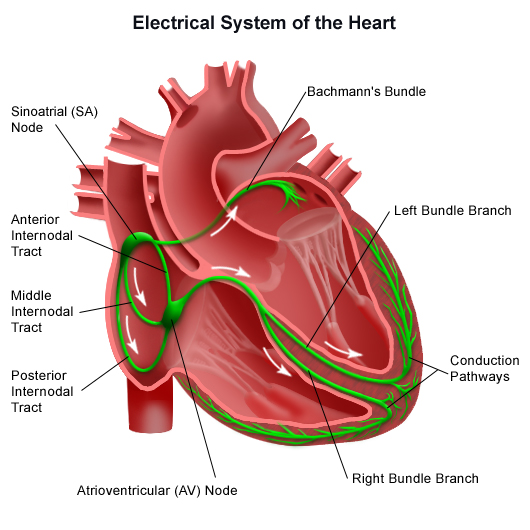
. For example the SA node increases the rate of impulses during exercise and decreases the rate of impulses during. The timing of the hearts contractions is directed by the hearts electrical system. A nerve impulse is a sudden reversal of the electrical gradient across the plasma membrane of a resting neuron.
Even if there are thin. A resting heart rate is normally 60 to 100 beats a minute. Though electrical continuity of such construction is normally not satisfactory for power frequency applications such as providing ground continuity it does not matter when using them for conducting lightning discharges.
Since the electrical stimulus begins at the apex the contraction also begins at the apex and travels superiorly toward the base of the heart similar to squeezing a tube of toothpaste from the bottom. The total time elapsed from the initiation of the impulse in the SA node until. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells called excitable cells which include neurons muscle cells endocrine cells and in some plant cells.
If the stimulus is strong enough to reach threshold an action potential will take place is a cascade along the axon. Atrioventricular block An interruption or disturbance of the electrical signal between the hearts upper two chambers the atria and lower two chambers the. In physiology an action potential AP occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls.
It begins when the neuron receives a chemical signal from another cell or some other type of stimulus. The electrical impulse begins in the sinoatrial SA node located in the right atrium. The reversal of charge is called an action potential.
This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Normally the SA node adjusts the rate of impulses depending on the persons activity.

Cardiac Muscle And Electrical Activity Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Anatomy And Function Of The Heart S Electrical System Johns Hopkins Medicine
0 Comments